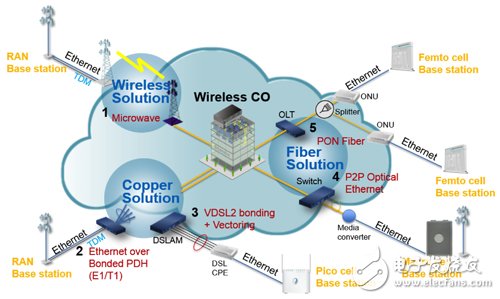
Fixed/mobile network convergence will enhance the competitive advantage of telecom operators. Under the rapid increase of mobile network data, telecoms can seamlessly extend the broadband network to any place through the seamless connection design of fixed network and mobile network, which can accelerate the deployment time and reduce maintenance costs. To further enhance market competitiveness. With the rise of smart phones and tablet computers, more and more users are connected to the network through mobile devices all the year round. Mobile phones are no longer just tools for talking phones. The services that consumers use to access mobile phones have been From traditional voice and SMS to data services such as entertainment, social networking and network interaction, consumers' reliance on mobile networks continues to deepen, and modern digital life is gradually taking shape. Any Content, Any Where, and Any Device have become the life style of the general public (Figure 1). Figure 1 Any Content, Any Where, Any Device new network life type According to the usage rate of mobile devices, the annual growth rate of global smart phone users is 42%, and the total number of users has exceeded 1.1 billion. However, this figure only accounts for 17% of global mobile phone users, and it is still quite large in the future. Growth space. Therefore, in the face of the surge in demand for mobile data services and the rapid growth of mobile device penetration, global telecom operators are accelerating their efforts to actively improve their wireless network infrastructure in response to the advent of the era of mobile broadband networks. How to build a next-generation mobile communication network to meet the rapidly growing bandwidth demand is the most urgent operational focus for telecom operators in the next few years. In order to provide high-bandwidth and high-quality network services for mobile communication devices, wireless mobile networks are evolving toward the next generation of fourth-generation mobile communication (4G) network technologies. In recent years, 4G Long-Range Evolution (LTE) has become the choice of telecom operators to deploy. The mainstream technology of wireless networks. Fixed/mobile network convergence is unstoppable The mobile network is heading towards 4G LTE, and the future mobile network base station will be dominated by a small cellular base station (Small Cell). According to market reports released by Informa Telecoms & Media, 98% of mobile telecom operators believe that Small Cell is indispensable for future mobile networks, and it is estimated that in 2015, the Small Cell Access Point will reach 6,000. Wantai. With the expansion of the 4G LTE Small Cell base station, another important issue has emerged: how to transfer huge broadband data traffic from the LTE base station backhaul (Backhaul) to the telecom equipment center (Central Office)? Therefore, the construction of broadband backhaul network (Mobile Backhaul) has become the key focus of the development of next-generation mobile networks. When the Small Cell is deployed in a large amount, it must use the wired broadband network as the Backhaul transmission. According to the InfoneTIcs market analysis, the mobile network Backhaul broadband transmission equipment business opportunity in 2016 will be as high as 9.7 billion US dollars, with a market size of NT$300 billion. Fixed Mobile Convergence (FCC), a combination of wireless 4G LTE and wired (fiber or copper) broadband networks, is expected to become an emerging mainstream solution for network construction in the next 10 years. Picking a mobile broadband network backhaul solution The era of fixed/mobile network convergence is coming. The deployment of Picocell can solve the problem of blind spots with poor wireless signals or insufficient hotspot bandwidth. However, the connection between the dispersed Picocell base station and the telecom equipment room is Another tricky issue. Mobile Backhaul transmission network line laying, equipment construction, network maintenance, etc., are far more difficult than deploying Picocell, and the investment is more. The most common solutions for Mobile Backhaul transmission networks are the following (Figure 2): 1. Connect to Picocell and telecom equipment room with digital subscriber line (DSL) copper transmission technology, with FTTx (Fiber To The x) fiber network such as next-generation synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) or 10Gigabit IP or passive optical network (PON). 2. Use the complete Fiber Network Architecture (Fiber All The Way) as the Backhaul network. 3. Use the microwave (Microwave) communication system as the Backhaul network. Figure 2 Mobile Backhaul transmission network common solution For telecom operators, the use of wired broadband networks as mobile networks for Backhaul transmission is a general trend. The barriers between fixed and mobile communication networks are gradually disappearing. The evolution of network convergence and technology represents the infinite possibilities of emerging services. Regardless of the digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) with copper wire as the transmission medium, or the PON and AcTIve Ethernet for fiber transmission, the future telecom operators will spend a lot of capital expenditure on the transmission network construction of Backhaul. (Capital Expenditures, CAPEX) and operating costs (OperaTIon Expenditures, OPEX), how to improve the bandwidth and quality of services, while effectively reducing CAPEX and OPEX, is the key to the competitiveness of mobile operators in various countries. Silicone Wire,Power Cord,High Temperature Line,Rubber Wire JIANGSU PENGSHEN HIGH TEMPERATURE WIRE CABLE CO., LTD. , https://www.pengshencable.com