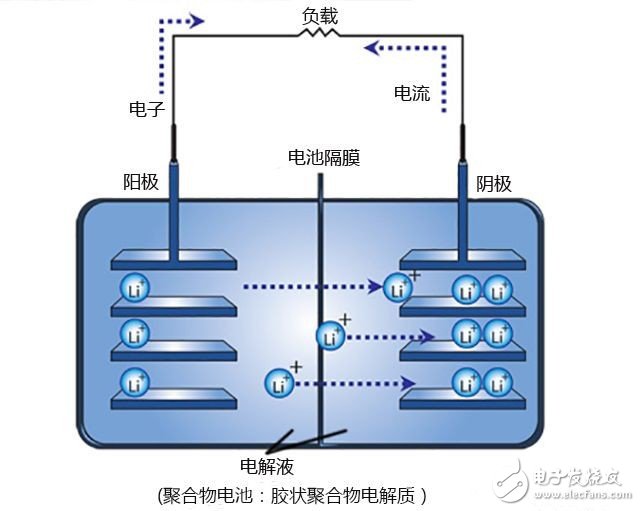
Before we start today's topic, let's take a look at how the internal lithium-ion battery works. In general, lithium batteries rely on lithium ions to transport electrons back and forth between the anode and cathode, generating electricity for use by external electronic devices. When the lithium battery is discharged, the lithium ions are first combined at the cathode and the electrons, and then the "loaded" electrons are transported to the anode and the cargo is unloaded to form a closed loop, generating an electric current; similarly, lithium ions are collected at the anode after discharge, when applied At the external current, the lithium ions of the "full load" electrons return to the cathode in the reverse direction after leaving the anode. Therefore, when all ions are in a high energy state, it means that the battery is fully charged. Discharge mechanism of rechargeable lithium battery The reason for the process of transporting electrons from lithium ions is analogous to the transportation of goods, because the items that need to be transported are usually placed neatly in the container, and a large number of electrons form a directional current. Since lithium ions in general lithium batteries exist in the form of monovalent electrons (Li1+), they can only be combined with one electron, but magnesium metal can be discussed separately. Normally, magnesium ions are present in the form of divalent cations (Mg2+), which means that if they act as "porters" in the battery, they can carry up to two electrons at a time. Therefore, in theory, if two batteries use magnesium ions and lithium ions of the same density respectively, the energy storage density of the battery using magnesium ion as the electron transfer medium will be twice that of the lithium battery. But then again, everyone knows that this theory does not necessarily apply to the reality. First, the most critical problem is that when magnesium ions are combined with two negative valence electrons, the entire nucleus has twice the negative charge, and the more negative the charge, the stronger the ability to attract other magnesium ions. . Therefore, when magnesium ions carry twice the charge and move between the two electrodes filled with electrolyte, the speed is naturally much slower. However, studies have shown that the problem that scientists are worried about may not have much impact. According to the experimental results of the report, it is proved that magnesium ions are only "bound" by four adjacent ions, which means that when magnesium ions pass through the poles of the battery, the maximum number of other ions that can affect their movement is higher than The previous estimate is small, so it doesn't seem to take too much trouble to solve this problem. The computer model shows that the magnesium ions in the electrolyte are only affected by four other neighboring ions.
The PufangTech`s wireless data modem is used to replace standard RS232 and RS485 serial communication cables. It provides a transparent connection between source and destination terminal and requires no knowledge of the data it is transmitting and the data can be simply sent and received with minimal delay.
With 12.5KHz channel spacing, the over-air transmission adopts different modulation scheme to meet various air rates. For air rate below 1200 bps, modulation scheme of FSK is used. For air rate of 1200, 2400 or 4800bps, MSK or FFSK modulation scheme is used. At 8000bps air rate, GMSK modulation scheme is adopted and at 9600bps air rate, the modulation is 4-level FSK. With 25KHz channel spacing, GMSK modulation scheme can support air rate of 16000bps and 4-level FSK can support 19200bps.
PufangTech`s wireless modem can make very beneficial and value added agreements with distributors and system integrators.
Wireless Data Modem,Wireless Radio Modem,Long Range Wireless Modem,Digi Wireless Modem Shenzhen PuFang Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hytelus.com