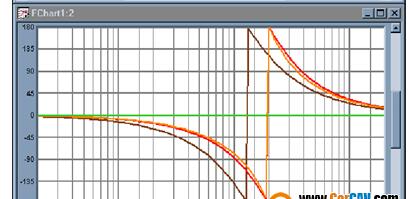
Professional audio technicians are not unfamiliar with the phase problem. The phase in the audio system is very abstract. This article first introduced the phase problem of the frequency divider in the speaker, and then explained the common phase problems and solutions in the audio system. Follow Xiaobian to find out. The frequency divider can be defined as: the input electrical signal is separated into two separate signals, and the bandwidth of each signal is smaller than the bandwidth of the original signal. Such a device consisting of one or more pairs of filters is called Frequency divider. It can also be called "frequency distribution network". The frequency divider is usually composed of a high pass (low cut) filter (HPF for short) and a low pass (high cut) filter (LPF for short). A filter is a frequency selection device that can block other frequencies from passing through the selected frequency. The filter usually has the following three parameters: cutoff frequency, network type, and slope. The cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the filter's response drops below a certain point below its maximum level, typically 0.707 times or 0.5 times the maximum level, or a frequency that drops 3dB or 6dB. The network type refers to the shape of the filter's frequency response curve near the cutoff frequency. In recent years, many types of filters have been designed. Common types of filters include: Batworth, Linkwitz, Bessel, etc. Figure 1 shows the frequency response curves of various filters. The slope is defined as the slope of the frequency response curve of the filter when it falls to the cutoff frequency. The unit is dB/octave, usually the slope is 6,12 per octave. , 18 and 24dB. Also known as 'filter slope' or 'filter order', the slope of the filter increases by 6dB/octave for each increase in the filter order, that is, the first-order filter has 6dB/octave. Slope, the second-order filter has a slope of 12dB/octave. Well, the 24W/octave Butterworth filter is equivalent to a 4th-order Butterworth filter. Figure 1: Red - 2KHz 24dB Linkwitz - Rayleigh high pass filter, orange - 2KHz 24dB Bad Wolf high pass filter, brown - 2KHz 24dB Bessel high pass filter, green - "-3dB", blue - "-6dB †Since the speaker unit does not have the same sound level, full-band output, the divider must be used in a full-range speaker system. The low frequency unit is used to reproduce the low frequency signal, the high frequency unit is used to reproduce the high frequency signal, and the frequency divider transmits the appropriate frequency signal to the appropriate speaker unit. Usually the divider is divided into active and passive. In general, the slave-separator splits the audio signal (speaker level) of the amplifier and is often used inside the loudspeaker. Active dividers separate the amplifier's audio signal (line level) before amplification, and are usually independent electronic devices located between the source and the amplifier. The signal passes through the divider and eventually flows into the corresponding speaker unit, which is used to reproduce the appropriate part of the sound spectrum. When the divider is designed, the signals of each speaker unit can be superimposed and the original input signal can be accurately reproduced. The divider will also affect some other parameters such as power, bandwidth, etc. These must be considered at design time. At a particular frequency, if the frequency responses of the two signals have similar amplitudes and slopes, the signals will add together to form a new signal. We can use the phase response to explain the difference in phase or the difference in the two signals. If the phase responses of the two filters are similar, the signals they output will add; otherwise, they will reduce each other. The different types and slopes of filters we discussed above all have their own unique phase response. Figure 2: Two identical filters. Orange - Normal, Blue - Reverse polarity. Although the two filters are the same in amplitude response, they have a clear difference in phase response. Careful observation will reveal that they have the same slope, a phase difference of 180 degrees, and it happens to be an inverted relationship. For a simple 180-degree phase shift, this should not be confused and can appear on a single frequency, as an example in Figure 3. Figure 3: Two identical filters. Orange - delayed, blue - normal. The difference in slope and phase is not fixed, but changes with frequency. This temporally offset or delayed characteristic can be used to indicate the difference between two devices. The performance of the combined speaker system (professional speakers) is closely related to the phase shift caused by the divider and the mounting position of the speakers. If the design does not pay attention to the phase shift problem, it is of no use to combine the other performance of the speaker. Eventually, distortion will occur and the frequency response curve will appear larger peaks and valleys. Usually, the phase shift caused by the installation position is : The phase shift of the -6dB/oct divider at the crossover point fc is 90°; The phase shift of the -12dB/oct divider at the crossover point fc is 180°; The phase shift of the -18dB/oct divider at the crossover point fc is 270°. For the -6dB/oct type divider, the tweeter can be delayed by 90° by adjusting the sound path difference between the radiating surface of the high and woofer speakers in the radiation direction so as to achieve high and low bass in-phase radiation in the radiation direction. For the -12dB/oct divider, because the phase shift at the frequency divider fc is 180°, the phase of the high and low frequency speakers can be reversed at the time of connection to ensure the same phase radiation. For the -18dB/oct divider, 270°=90°+180°, it can be adjusted in combination with the above two methods. I. Some phase problems often encountered in actual acoustic engineering 1, speaker unit phase After the audio signal with the same frequency is output from the power amplifier, if one pair of speakers has one phase inversion (usually referred to as “+†and “-â€), then the elements of the pair of speakers will have an AC phase difference and the audio signals will cancel each other out. After the sound reinforcement, the low-frequency signal is obviously weak, the sound becomes hard and dry, and the high-frequency waves will go back and forth, affecting the debugging and overall effect of the entire sound reinforcement system. 2, power amplifier phase problem It is easier to understand the positive and negative poles of the output terminal after using the four-core plug. The banana output plug also has obvious red and black ports for identification, but when the power amplifier uses bridge, pay attention to the red end of the signal input control (usually A-transmission). For positive, the red end of the other input control (usually the B channel) is negative. 3, the audio system power phase If the power used by a system device is out of phase (for example, if the amplifier is powered by the A-phase, or the mixer is used to supply power from another phase), the difference between the high and low phases occurs when the power consumption of the device is not uniform. , It will cause some equipment voltage is high or low to cause the work not to be normal, bring about some interference to the whole system effect, such as: The buzz sound, electric current sound,etc.; It may also cause the equipment damage because the phase difference is too big. 4, audio pickup section The microphone also has a phase. If there are multiple microphones used at the same time, there is a microphone inverting phase, which will lead to an unbalanced feeling in the overall sound pickup. The closeness of the pickup microphone will cancel the signal. When the two microphones with the same phase are picked up at a short distance, it is easy to cause signal overlap, increase the generation of positive feedback, and generate self-excitation. This phenomenon is more common in Karaoke. At the same time can be a test, the same phase of the two dynamic microphones, to 180 ° relative to pick up, will obviously feel the sound pressure is low, or no signal output. 5, good grade mixer Generally, there is a phase change switch. When using several microphones of different types to pick up the sound in parallel, if abnormal or weak sound is found, the phase change switch of one of the microphone channels can be pressed to judge whether the phase problem is caused. When the two singers sing together in "deep affection", if the handheld microphone is close to a relatively horizontal position, you will find that the pickup signal is reduced. Now pressing one of the microphone phase shift switches can solve this problem. Second, the method to solve the phase problem in professional audio engineering As a technician working in a professional sound reinforcement project, if there is a reverse phase in the system, this is simply unacceptable because there is only one explanation. Your speaker cable is reversed (or the signal wire is reversed), except for inferior products. In addition, the possibility of phase reversal between the speakers themselves and the power amplifiers is very low. In our work, the main problem related to the "phase" touched is often the reverse phase. The phase shift is rarely encountered unless we design the divider or audio signal processing circuit ourselves. For example, a treble string of capacitors has a phase difference of 90 degrees. While inversion is easy to find in practical applications, there are two simple ways to solve this problem: 1, for the phase problem in the circuit, now the domestic phase detector has been very cheap, less than 300 yuan. There are various interfaces such as Canon, RCA, 6.3 DIP, and so on, which can directly detect whether there is an inversion problem in the line. However, they cannot all be linked together at the end of the test, because if there are two strings in the middle of the series, they are negative and positive. It should be measured for a while. This should be a procedure that must be followed in the project installation. 2, for the amplifier to the speaker is inverted, you can directly determine by hearing. If you feel that you do not have this confidence, you can send a mono signal to both channels of the mixing console at the same time, and then position them on the left and right channels through the PAN (Pan Positioning Knob) and then through the mixing console. The left and right main outputs are sent to the left and right speaker groups. Then keep the phase of one of the two input channels unchanged, and the other channel uses the phase switch button to reverse-switch. If the low-frequency is full and powerful and the mid-frequency is full, there is no problem with the phase. In the sound reinforcement system, due to the reversed polarity of the microphone signal output line or the speaker power signal input line and the phase distortion of the system, various types of reverse phase or phase shift of the sound may be caused. Whether the sound phase relationship is correct or not (especially reversed phase) will directly affect the sound reproduction quality. However, at present, many small and medium-sized audio engineering technicians in China do not seem to pay much attention to the reversed phase of the system. Most audio workers will not consider the phase of the microphone and speaker after connecting the system; nor will they consider the series of phase distortions that may be brought about by the adjustment during the equipment and system adjustment. This is for modern audio systems. It is undoubtedly a shortcoming. I hope that this article can give more attention to friends engaged in the application of small and medium-sized engineering and technology.
400W 20-port USB 4*C+16*A port charger, support PD QC2.0 QC3.0 support 5V\9V/12V free transform.fo apple, Android,ipad.
Type C Fast Charger 20 Port 400W 4A USB PD Charger Adapter Type C Quick Charging For iPhone Samsung EU UK Plug.
20 ports USB charger is portable and includes 4 USB Type-C ports and 16 USB Type-A ports. The USB-A ports have a Maximum of 2.4A with a Maximum of 3A for the USB-C ports. This USB C and A combo charger is versatile accepting both USB C and USB-A dependent devices. All ports can be used simultaneously with its built-in Smart IC chip power detection of low and high power requirements.
20 Port Type-C Charger,Type C Fast Charger 20 Port,20 Ports 4PD+16QC Charger(400W),400W with 4 USB-C and 16 USB-A Ports shenzhen ns-idae technology co.,ltd , https://www.szbestchargers.com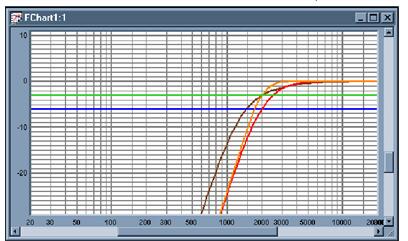

USB 20 Port Charger 400W supplies a 2.4A charging current for iPads, Tablet PC`s, Samsung Tablets, or other with dedicating two additional USB ports for charging 1A devices such as, iPhone, Nexus, or Windows Phones.