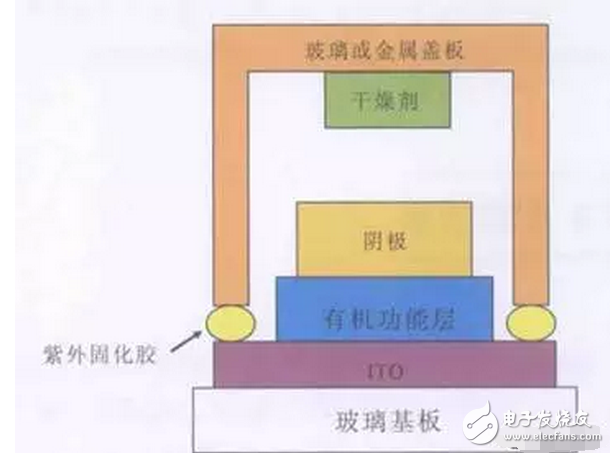
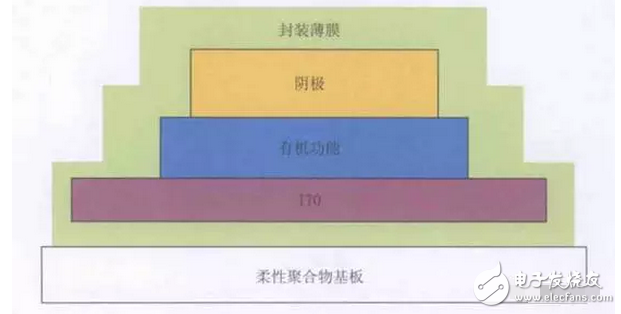
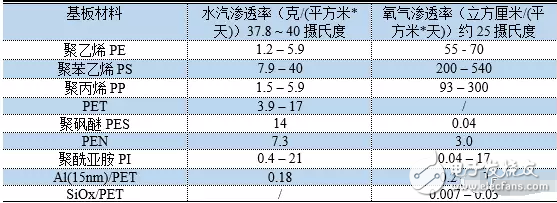
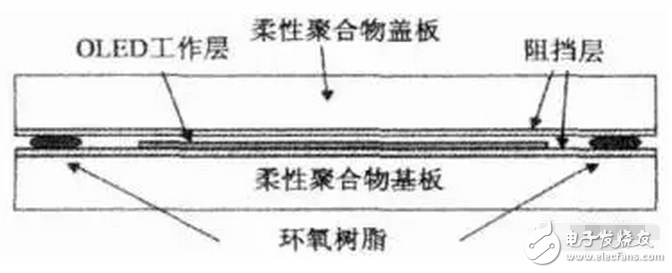
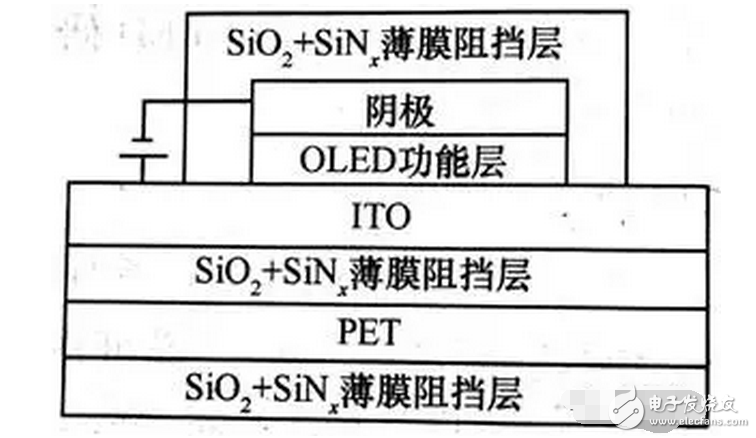
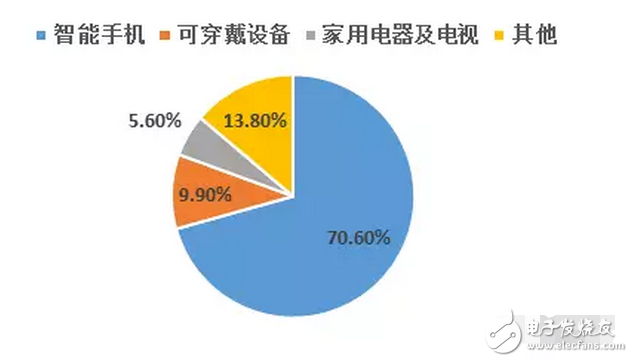
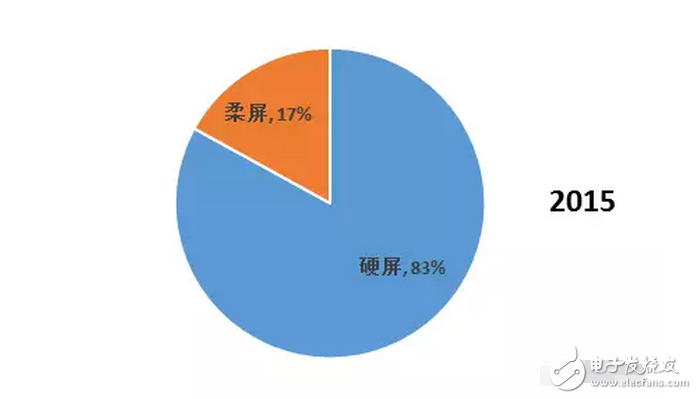
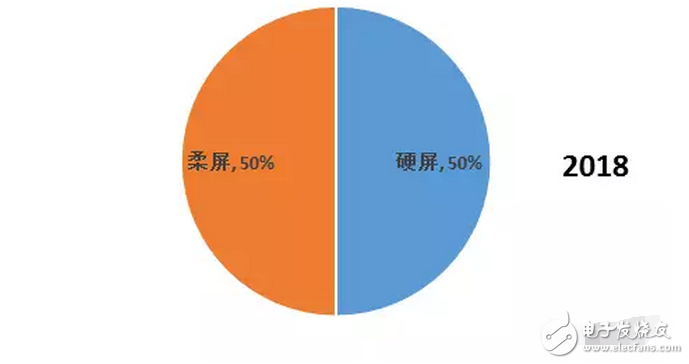
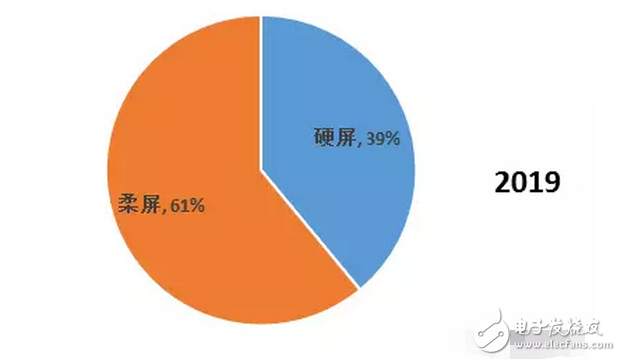
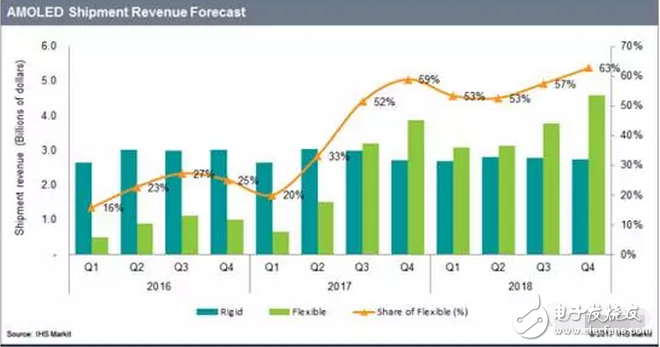
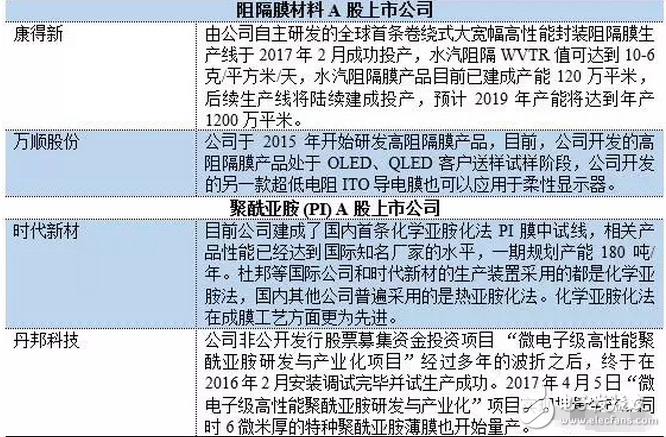
Due to the differences in structure, material properties and illumination principles between OLEDs and TFT-LCD devices, OLED light-emitting devices are more suitable for the manufacture of flexible screens – Flexible Screens. The current flexible screen is also widely known as a curved screen because it only presents a fixed curved surface, which does not seem to be "flexible" because the glass material needs to be maintained due to the screen, and the glass material has its insurmountable curvature. obstacle. The "flexible" screen is currently moving in both "Bendable" and "Foldable" directions, but the ultimate goal is to achieve a "Rollable" screen. Figure 1 "Bendable" screen renderings The "curved surface" OLED screen for the initial stage of the flexible screen has also brought about several new explorations in design and processing. The most important ones include the cover glass to be upgraded from 2D to 3D, and the touch technology has changed. Changes in the packaging process. The last and most critical one is because it is directly related to the yield of flexible screens, which in turn affects the process of mass production. At present, the most commonly used OLED hard-screen packaging is glass-based glass or metal cover packaging, while flexible devices are packaged in single-layer and multi-layer thin films. Figure 2: Cover-type package with UV-curable adhesive bonded to glass (OLED display base and industrialization) Figure 3 Blocking package with polymer as substrate (OLED display base and industrialization) OLED has a fatal weakness, fearing that oxygen is afraid of water. Once oxygen or water vapor enters the device, it will cause a decay in device life. Therefore, for flexible OLED devices, the lifetime problem depends on the barrier properties of the flexible substrate and packaging technology for oxygen and moisture. Based on this principle, the substrate material of a flexible OLED can have three options: ultra-thin glass, metal foil, and polymer. Basic boron glass containing cerium oxide or aluminum oxide can be used as ultra-thin glass, and pure boron glass can also be used as ultra-thin glass. Since ultrathin glass is very thin and brittle, a polymer layer is required to protect the glass surface so that the glass is not damaged by external force and corrosion of chemical agents. Metal foils exhibit excellent properties in thin film packaging. When the thickness of the metal material is less than 0.1 mm, it has superior bendability and can be used for a flexible OLED substrate. Moreover, it has excellent high temperature resistance and can withstand high temperatures of over 1000 degrees Celsius; the coefficient of thermal expansion is more compatible with glass and polymer, and fewer problems may occur during the production process; excellent resistance to oxygen and water vapor can effectively prevent two Intrusion. However, metal foil as a flexible OLED substrate also has two problems: First, the transmittance of the metal foil to light is almost zero, so the OLED device with the metal foil as the substrate can only adopt the top light-emitting structure; The surface roughness of the sheet is poor, and it is necessary to increase the combination of mechanical polishing and electrochemical polishing to solve the problem, and then it is necessary to add a SiOx dielectric layer to lower the surface roughness. The polymer substrate is more flexible and more resistant to impact than glass and metal foil. However, the polymer substrate cannot withstand higher temperatures. In addition, the polymer substrate has a poor surface flatness compared to glass, and the success rate of preparing the conductive electrode on the polymer substrate is low and the resistivity is large. Therefore, the polymer substrate material used for OLED needs to consider the following three problems: 1. It should have a transmittance of more than 95% in the visible light range; 2. The physical and chemical properties of the polymer, such as thermal UV stability and Yang Modulus, etc.; 3. Improve the barrier properties of the polymer for harmful gases, and the success rate of preparing electrodes on a polymer substrate, and reduce the resistivity. The quality of OLED package has a great relationship with the flatness of the base material. Flexible OLEDs mostly use polymer instead of glass as the substrate. At present, the main substrate materials are polyacrylates (polyacrylate) and PETS (polyethylene terephthalate). Alcohol ester), fluorinated-polymers (fluorinated polymer), PEN (polyethylene naphthalate), parylenes (parylene), PC (polycarbonate), etc., these materials are for water vapor and oxygen. The permeability is listed in the table below. Table 1 Permeability of polymer substrate materials to water vapor and oxygen In fact, the polymer materials in the table can not meet the requirements of current applications, and the high water vapor permeability is a fatal defect of all polymer substrates. According to the packaging requirements of flexible OLED devices, it is necessary to prepare one or more layers of high barrier protective layers on the surface of the polymer. In order to reduce the infiltration of moisture and oxygen into the interior of the device through the polymer substrate, it is usually achieved by depositing a multi-layered stacked inorganic film on the surface of the flexible substrate, or by sticking a barrier film. The barrier film material includes SiO2, Si3N4, SiNxOy, Al2O3, AlN, Mg, and the like. The barrier film is generally based on a flexible polymer substrate on which an inorganic oxide is deposited on a substrate by magnetron sputtering, electron beam evaporation or plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition to form a vapor barrier film. . Figure 4: Polymer-based barrier package Figure 5 Schematic diagram of SiO2 + SiNx film package with PET as substrate OLED is currently mainly used in smart phones, household appliances and televisions, and products including smart watches, VR devices, etc., of which the highest proportion of applications in smart phones, reaching 70.6%. The key advantage of OLED lies in its flexibility, achieving "flexible" display, and increasing the application scene and imagination of traditional display screens. Especially after the Samsung production of the Edge mobile phone series realized the display of the curved screen. The current iteration of smartphone LCD screens is the main driver for OLED screen growth. Figure 6 OLED application distribution (Source: China Industry Information Network) Figure 7 Samsung Edge Surface Phone In terms of product form, in 2015, 83% of AMOLED screens in the world are hard AMOLEDs, but based on the revolutionary innovation brought by flexible screens to display screens, market consultancy TrendForce predicts 2018 "flexible" and "hard" AMOLED screens. The production capacity will be equally divided, and by 2019 the flexible screen capacity will be over-hardened, reaching 61%. Qunzhi Consulting also predicts that based on the currently established flexible OLED investment production line, the penetration rate of flexible AMOLED will stabilize at around 65% by 2019, while rigid OLED will no longer have new growth. At present, Samsung has built 8 flexible AMOLED generation lines, and Apple has decided to apply flexible AMOLED screens in the iPhone 8. Figure 8 2015/2018/2019AMOLED flexible screen and hard screen capacity Source: TrendForce Figure 9 2016-2018 Percentage of flexible screens in OLED screen shipments Source: IHS The consulting firm IHS made a more optimistic forecast for the growth trend of OLED flexible screen sales in the next two years. It believes that in the third quarter of 2017, the sales of OLED flexible screens will be anti-hard screen, reaching 52% of total sales. And its penetration rate will remain above 50% after this, and maintain the overall growth trend, which will reach 63% in the fourth quarter of 2018. With the rise of flexible screens, the market for polymer substrates and water vapor and oxygen barrier materials has gradually expanded. Among them, the internationally famous commercial production and production companies of barrier films are American Vitex System, 3M, GE, etc. Vitex System has developed Barix technology, which is formed by alternately forming organic and inorganic materials. The properties of the Barix barrier layer can be controlled by varying the number and composition of the polymer and inorganic film. Among the domestic listed companies are Kangdexin and Wanshun shares. The current mainstream application of polymer substrates is high temperature resistant polyimide (PI), mainly from DuPont (USA), Ube Industries (Japan), Zhong Yuan Chemical (Japan), Toray-DuPont (Japan). ) and five companies such as SKC (Korea) are monopolized. Among the domestic listed companies are Times New Materials and Danbang Technology. China's high-end PI film demand is about 5,000 tons, and the market space is more than 5 billion yuan, which is mainly monopolized by foreign-funded enterprises. At present, domestic enterprises mainly do relatively low-end electrical-grade products, and the product quality is far from the foreign products such as DuPont. Table 2 Domestic major barrier film materials and polyimide A-share listed companies
3. The screws are not loose
Busbar Marine Terminal Block,Screw Busbar Insulators,Electrical Drum Support Busbar,Battery Support Busbar Wonke Electric CO.,Ltd. , https://www.wkdq-electric.com

First, the manufacturing difficulties and solutions of OLED flexible screen
1. Can be fixed on two kinds of guide rails
2. Since it is inserted into the guide rail, the
terminal pressing block is absolutely reliable
1. Can be fixed on two kinds of guide rails
2. Since it is inserted into the guide rail, the
terminal pressing block is absolutely reliable
3. The screws are not loose
Two kinds of holders made from insulating
materials:
1. One layer holder AB/SS (with screws) for
one busbar.
2. Double layer holder AB2/SS which are
arranged staggered on both sides of the N-line
and PE-line busbars.